|
| What are the mesothelioma causes? |
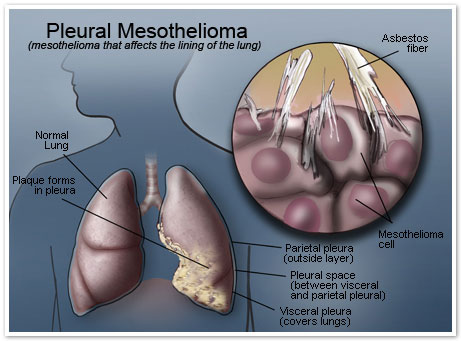
Working with asbestos is the most common risk factor for mesothelioma.In the United States, asbestos is considered to be the leading cause of malignant mesothelioma and has been considered "indisputably" associated with the development of mesothelioma. Indeed, the relationship between asbestos and mesothelioma is so strong that many view mesothelioma as a "signal" or "sentinel" tumor.The history of exposure to asbestos exists in most cases. However, mesothelioma has been reported in some individuals without known exposure to asbestos. In rare cases, mesothelioma has also been associated with irradiation of the chest or abdomen, intraplaural thorium dioxide (thorotrast) as a contrast medium, and inhalation of other fibrous silicates, Erionite or talc. Some studies suggest that simian virus 40 (SV40) can act as a cofactor in the development of mesothelioma. This has been confirmed in animal studies but studies in humans are inconclusive. Pericardial mesothelioma may not be associated with exposure to asbestos.
Asbestos was known in antiquity, but it was not exploited and widely used commercially until the late 19th century. Its use increased considerably during the Second World War. Since the early 1940s, millions of American workers have been exposed to asbestos dust. Initially, the risks associated with exposure to asbestos were not publicly known. However, an increased risk of developing mesothelioma was later found in marine personnel (eg, the Marine, Marine Corps and Coast Guard), shipyards, miners and Asbestos mills, asbestos producers, heating and construction workers Industries and other traders. Today, the official position of the US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the US EPA is that the protections and "permissible exposure limits" required by regulations American, while being adequate to prevent most non-malignant diseases related to asbestos, are not adequate To prevent or protect against asbestos-related cancers, such as mesothelioma. Similarly, the UK Health and Safety Executive (HSE) formally states that any exposure threshold for asbestos must be at a very low level and it is widely Such threshold exists, it can not currently be quantified. For practical reasons, therefore, HSE assumes that a "safe" threshold does not exist. Others also noted that there is no evidence of a threshold below which there is no risk of mesothelioma. There appears to be a linear relationship, dose-response, with an increase in dose producing a growing disease. Nevertheless, mesothelioma can be linked to brief exposures, weak or indirect asbestos. The dose needed for the effect appears to be lower for asbestos-induced mesothelioma than for pulmonary asbestosis or lung cancer. Again, there is no known safe level of exposure to asbestos with regard to the increased risk of mesothelioma.
The duration of exposure to asbestos causing mesothelioma can be short. For example, cases of mesothelioma have been documented with only 1 to 3 months of exposure. Individuals who work with asbestos wear personal protective equipment to reduce their risk of exposure. [Citation needed]
The latency, the moment of the first exposure to the manifestation of the disease, is prolonged in the case of mesothelioma. It is virtually never below fifteen years and peaks at 30-40 years. In a review of work-related mesothelioma cases, the median latency was 32 years. Based on data from Peto et al., The risk of mesothelioma appears to increase at the third or fourth power from the first exposure.